ADVERTISEMENT
Welcome to our blog where we will be discussing about edge computing, a rapidly growing technology with huge potential to transform the way we run businesses and access information.
In today’s digital era, speed, efficiency, and storage capacity are crucial for improving system performance. This is why edge computing has become an interesting topic to discuss. Keep reading to understand what edge computing is, how it works, and why this technology is so important.
The definition of Edge Computing
What is Edge Computing?
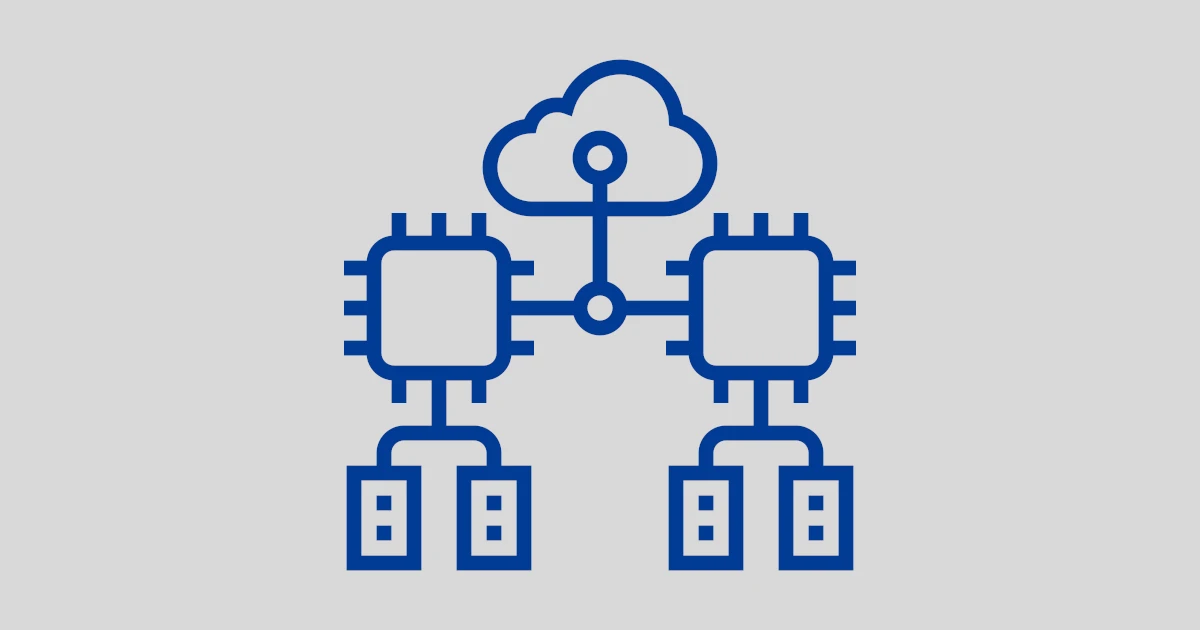
Edge computing is a computational model designed to help improve efficiency in communication systems by reducing latency. The basic principle of edge computing is data processing that is done near the source of the data, which is called the “edge” of the network. This means that data is processed by devices or systems that are closer to the point where the data is generated, such as sensors, cameras, or IoT devices. The main goal of this approach is to increase system responsiveness and minimize the load on wider network infrastructure.
Instead of sending raw data to a data center or cloud for processing, edge computing enables data processing locally, thus reducing latency caused by distance. By reducing latency, systems can respond more quickly to changing conditions and meet the needs of applications that require real-time responsiveness. This approach also reduces the load on networks and data centers, saving bandwidth and improving overall system performance. Therefore, edge computing has become an attractive solution in contexts such as the Internet of Things (IoT), autonomous vehicles, and Industry 4.0.
Why is Edge Computing Important?
The importance of edge computing lies mainly in its ability to reduce latency in data processing, which is a critical factor in many modern applications. By placing data processing closer to its source, edge computing minimizes the distance that data must travel between devices and processing centers. As a result, the time required to send and receive information becomes much shorter, improving system efficiency overall. This approach is especially beneficial in situations where high speed and responsiveness are crucial.
Applications that require fast response times, such as automated control systems and the Internet of Things (IoT), greatly benefit from the use of edge computing. In automated control systems, for example, fast and timely decisions are crucial to maintaining system reliability and security. Meanwhile, in the IoT environment, millions of connected devices generate vast amounts of data that need to be processed and analyzed efficiently. By processing data at the “edge” of the network, edge computing enables faster responses to changing conditions and meets the needs of applications that rely heavily on high speed and performance.
How Does Edge Computing Work
Data Processing at the ‘Edge’ of the Network
The basic principle of edge computing is relatively simple and is based on the idea of processing data near its source. When data is generated by a device, such as a sensor or camera, instead of sending raw data to the cloud or data center, the data is processed by a device located near the data source. This device, known as an edge device, can be a microcontroller, single-board computer, or edge server. This process allows for initial analysis and data processing to be done locally before the data is sent further.
After the data is processed by the edge device, the results of this processing, which are often in the form of summary information or insights, are then sent to the cloud or data center for storage or further analysis if needed. By reducing the amount of raw data sent over the network, edge computing effectively reduces the load on network infrastructure and improves overall performance. Additionally, this also saves bandwidth and computing resources, thereby increasing efficiency and reducing operational costs.
Edge Computing Devices and Infrastructure
The infrastructure of edge computing consists of various hardware devices required to process data near its source. Some examples of hardware devices in edge computing include edge servers, which are high-performance processing servers located near devices that generate data; IoT gateways, which act as a connection point between IoT devices and wider networks; and micro data centers, which are small-scale data centers designed to provide data processing and storage services in locations close to the data source. These hardware devices play a critical role in ensuring that data is processed quickly and efficiently.
On the software side, edge computing involves the use of applications designed to work in low-latency environments and optimized operating systems for speed and efficiency. These applications are able to process data in real-time, make decisions based on the information received, and communicate with other devices in the network. Meanwhile, operating systems optimized for edge computing are often designed to reduce overhead and improve performance, allowing hardware devices to function more efficiently. In combination, these hardware and software devices form a strong and flexible infrastructure capable of supporting various edge computing applications in various industries and use case scenarios.
Benefits of Edge Computing
Gains in Speed and Efficiency
One of the main benefits offered by edge computing is the improvement in speed and efficiency in data processing. By processing data near its source, edge computing reduces the latency generated by the distance that data travels between data-generating devices and processing centers. As a result, systems that use edge computing are able to respond more quickly and efficiently to user requests. This higher speed and responsiveness are crucial in various applications that require fast response times.
Examples of applications that greatly benefit from the speed and efficiency offered by edge computing include automated control systems, healthcare services, and security. In automated control systems, fast and timely decisions are crucial to maintaining system reliability and security. In healthcare services, edge computing can help improve the quality of care by enabling real-time patient monitoring and faster responses to emergencies. Meanwhile, in security applications, the use of edge computing allows security systems to more quickly detect threats and respond to suspicious events, thus increasing the level of protection provided to users and protected assets.
Reducing Load on Networks and Data Centers
Another benefit offered by edge computing is the reduction of load on networks and data centers. By processing data closer to its source, the amount of raw data that needs to be sent to data centers or the cloud is reduced. Data that has been processed at the edge device is usually more compact, having undergone preliminary analysis or processing. By reducing the volume of data that needs to be sent over the network, edge computing effectively reduces the load on network infrastructure and reduces the likelihood of congestion or delays in data communication.
Furthermore, reducing the load on the network also has a positive impact on overall system reliability. By reducing the risk of network failure or performance degradation due to excessive load, edge computing helps improve system stability and reliability. This allows applications and services that depend on smooth and fast data communication to function more efficiently and reliably. In the long run, this approach results in a better user experience and increased customer satisfaction, as well as helping companies reduce operational and network maintenance costs.
Edge Computing Application
Edge Computing in the Internet of Things (IoT)
One of the main applications of edge computing is in the field of Internet of Things (IoT), which involves millions of interconnected devices such as sensors, cameras, and smart devices. IoT generates a large amount of data that needs to be processed, analyzed, and controlled to ensure optimal system performance. In this context, edge computing plays a crucial role in improving the efficiency and speed of response of IoT devices by processing data near the source, allowing devices to respond more quickly to changes in conditions or important events.
Furthermore, the use of edge computing in IoT also has a positive impact on network loads. By processing data at the edge, the amount of data that needs to be sent to a data center or the cloud is reduced, which in turn reduces the load on the network infrastructure. This allows larger IoT networks to function more efficiently, reducing data congestion and saving bandwidth. In the long run, this helps improve overall IoT system performance, ensuring faster responses and better user experiences, and helping companies reduce operational costs and network infrastructure.
Edge Computing in Industry 4.0
Industrie 4.0 is a revolutionary concept that combines digital technologies, such as IoT, artificial intelligence (AI), and edge computing, to create smarter, more efficient, and connected production systems. In an industry heavily reliant on this technology, the role of edge computing becomes crucial in optimizing production and operational processes. One main aspect where edge computing plays a vital role is in processing data generated by industrial devices such as sensors and robots that constantly collect information about machine conditions, environments, and system performance.
By processing this data near the source, edge computing allows companies to make better and faster decisions based on accurate and real-time information. This helps in reducing machine downtime, improving efficiency, and optimizing production processes. Additionally, edge computing also enables companies to more easily integrate advanced AI technology and data analytics, which can be used to identify patterns and trends in data and provide valuable insights that can be used to improve business processes and strategies. In the long run, implementing edge computing in the context of Industrie 4.0 helps companies achieve unprecedented levels of flexibility, speed, and innovation, which ultimately impacts competitiveness and business growth.
Challenges in Edge Computing
Data Security and Privacy
One of the main challenges in edge computing is data security and privacy. Because data is processed near its source, there is a risk that data can be intercepted or compromised by unauthorized parties. Additionally, because edge computing devices are often located in more accessible locations than secure data centers, they are vulnerable to physical or software attacks that can result in data loss or theft. Therefore, security is one of the top priorities in designing and implementing edge computing systems.
To address these security and privacy concerns, companies must implement strong security solutions to protect their data. Some steps that can be taken include using data encryption, which ensures that data sent between end devices and data centers or clouds cannot be read by unauthorized parties; implementing authentication and authorization technologies to limit access to devices and data; and continuous monitoring and management of security to detect and address threats before they cause damage. Additionally, companies must keep their software up-to-date and implement best practices in system design and network configuration. By combining these security measures, companies can minimize the risks associated with edge computing and ensure that their data remains safe and protected.
Infrastructure Management and Maintenance
Managing and maintaining edge computing infrastructure can be a challenge, especially since devices may be distributed across different locations, often with varying environmental conditions and limited access. This poses challenges in monitoring device performance, identifying issues, and performing maintenance or repairs in a timely manner. Therefore, companies need to invest in efficient management solutions that enable them to monitor, control, and optimize the performance of edge computing devices in real-time and remotely.
To address this issue, companies can adopt technologies such as a centralized management system that allows them to manage endpoint devices from a central location. This system can provide information about device performance, identify issues, and enable administrators to take corrective or repair actions remotely. Additionally, companies should also consider automating device maintenance, using technologies such as artificial intelligence and data analysis to predict maintenance needs and optimize maintenance schedules. By combining efficient management solutions and device maintenance automation, companies can ensure that their edge computing infrastructure remains functional and efficient, while reducing operational and maintenance costs in the long run.
The Future of Edge Computing
Edge Computing Technology Development
In the coming years, edge computing technology will continue to evolve, thanks to ongoing research and development in this field. Innovations will result in improvements in efficiency, speed, and storage capacity of edge devices, as well as the ability to support more complex applications that require higher resources. With these technological advancements, companies will have greater opportunities to leverage edge computing in various applications, from IoT to Industry 4.0, and beyond the sectors that are already using this technology today.
As a result of this development, we will see edge computing becoming a more integrated part of a company’s IT architecture, as well as a critical component in their digital strategy and business innovation. The development of edge computing will enable companies to be more efficient in managing the data generated by connected devices, as well as improving the performance and reliability of their systems as a whole. In addition, the development of edge computing will open the door to new applications that were not possible before, such as real-time analytics, edge-level artificial intelligence, and more advanced security solutions. In the long run, advancements in edge computing technology will have a positive impact on various industries and help shape the future of information and communication technology.
Merger with Other Technologies
The future of edge computing is likely to see a merger with other technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). This integration will enable edge devices to process and analyze data in a more sophisticated way, leveraging AI and ML algorithms to automatically identify patterns and trends in data. By integrating these technologies into edge computing, companies will be able to uncover deeper insights from their data and make smarter decisions based on that information.
This will open up new opportunities for advanced data analytics and real-time data-driven decision-making, which will further improve system efficiency and performance. For example, in industries such as manufacturing and logistics, the integration of AI and ML with edge computing can help optimize production and distribution processes, reduce costs, and improve product reliability. Similarly, in sectors such as healthcare, the use of AI and ML in edge computing can aid in more accurate and timely diagnosis and treatment, as well as improving the quality of patient care. Overall, the combination of edge computing, AI, and ML will bring about significant changes in how companies use technology to enhance operations and gain a competitive edge in the market.
Edge Computing Use Cases
Smart Cities
Edge computing plays a significant role in the development of smart cities. In the context of smart cities, various sensors and IoT devices are used to collect data on various aspects of urban life, ranging from traffic to energy consumption and security. By processing this data near its source, edge computing reduces latency and allows governments and companies to take action more quickly based on the information received. This enables more efficient management of city infrastructure, as well as improving the quality of services provided to citizens.
In addition, edge computing also supports the integration of various systems and platforms in smart cities, such as transportation systems, security systems, and energy management systems. By enabling faster and more efficient communication between these systems, edge computing helps to create a more interconnected and responsive environment, which ultimately leads to an improvement in the quality of life for city residents. For example, edge computing can help optimize traffic flow by processing real-time data from cameras and sensors, reducing congestion and air pollution. Similarly, in energy management, edge computing can support the use of renewable energy sources and optimize energy distribution throughout the city. Therefore, the role of edge computing in the development of smart cities will continue to grow alongside technological advancements and the need for innovative solutions in urban infrastructure management.
Autonomous and Autonomous Vehicles
In the automotive industry, edge computing is used to improve the speed and accuracy of autonomous vehicle systems. Autonomous vehicles require fast and efficient processing of data from various sensors and cameras to make decisions about navigation, acceleration, braking, and other maneuvers. Edge computing allows this data to be processed in real-time near its source, reducing latency and allowing the vehicle to respond more quickly to changes in road and environmental conditions.
The implementation of edge computing in autonomous vehicles not only improves safety but also efficiency. For example, edge-optimized algorithms can help autonomous vehicles dynamically adjust routes to avoid traffic congestion, reduce fuel consumption, and speed up travel time. Additionally, edge computing allows autonomous vehicles to communicate efficiently with road infrastructure and other vehicles, such as smart traffic light systems or integrated traffic management systems. Thus, the integration of edge computing in the automotive industry will continue to help drive innovation and the development of more safe, efficient, and reliable autonomous vehicle systems.
Tips for Choosing an Edge Computing Solution
Evaluating Business Needs
It is important to evaluate business needs and determine goals before choosing an edge computing solution. Each business has unique and specific needs, so it is important to understand how edge computing technology can help achieve those business goals. Consider factors such as the type of data to be processed, data volume, processing speed needed, as well as data security and privacy. Understanding these needs will help you make a more informed decision in choosing the edge computing solution that is most suitable for your business.
After identifying business needs and goals, you can determine the features and capabilities required of the edge computing solution you choose. Some features that may need to be considered include scalability, integration with existing systems and devices, support for stringent security standards, and ease of management and maintenance. Additionally, you may want to consider solutions that offer flexibility in terms of architecture and service provider options, as well as support for the latest technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning. By considering these features and comparing different solutions, you will be able to choose the edge computing solution that is most suitable to support the growth and success of your business.
Comparing Vendors and Technologies
After evaluating business needs, the next step is to compare vendors and technologies available in the market. In this stage, it is important to conduct thorough research on various edge computing solution providers and understand the features and advantages offered by each. Pay attention to the vendor’s experience and reputation in the industry, as well as testimonials and case studies available to provide an overview of customer satisfaction and performance. Conducting comparative analysis will help you assess the reliability, scalability, and technological innovation offered by various vendors.
In addition, consider other factors such as support and cost when choosing the edge computing solution that is most suitable for your business. Effective and responsive support from the vendor is crucial to ensure the smooth operation and maintenance of the edge computing infrastructure. Check if the vendor offers adequate technical support, such as 24/7 support, access to experts, and fast response times. Meanwhile, cost is also a key consideration in choosing an edge computing solution. Compare initial costs, operational costs, and licensing costs from various vendors to determine the most cost-effective solution in terms of investment. By considering all of these factors, you will be able to make the right decision in choosing the edge computing solution that is most suitable for your business needs and budget.
Conclusion
Edge computing is a technology that offers many benefits, including increased speed, efficiency, and reduced load on networks and data centers. However, there are also challenges to be faced, such as data security and infrastructure management. By understanding the basic principles, applications, and future of edge computing, businesses can better leverage this technology to improve system performance and achieve their business goals.
ADVERTISEMENT